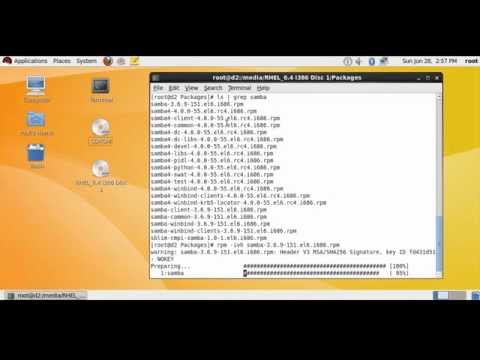
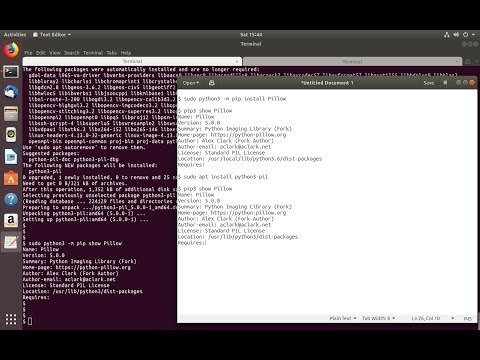
It additionally updates established profiles in the event that they can be found for the brand new stream. When a profile was provided, it installs that profile and doesn't replace any already established profiles. Will attempt to dispose of all packages with a reputation similar to the packages established with a profile or a stream, together with their dependent packages. Always test the record of packages to be eliminated earlier than you proceed, above all when you've got enabled customized repositories in your system. In variations in advance of 1.9.2 this module established and eliminated every package deal deal deal deal deal given to the yum module separately.
This induced issues when packages specified by filename or url needed to be set up or eliminated together. In 1.9.2 this was fastened in order that packages are set up in a single yum transaction. DNF is a software program program package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal deal supervisor that installs, updates, and removes packages on Fedora and is the successor to YUM (Yellow-Dog Updater Modified). DNF makes it straightforward to keep up packages by routinely checking for dependencies and determines the actions required to put in packages. This technique eliminates the necessity to manually set up or replace the package, and its dependencies, utilizing the rpm command. DNF is now the default software program program package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal deal administration device in Fedora.
The record command additionally limits the displayed packages in accordance with detailed criteria, e.g. to solely people who replace an set up package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal . All Python package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal administration options present the essential perform of uninstalling packages, consisting of pip, pipenv and the ActiveState Platform. However, until particularly outlined in a requirements.txt or pipfile.lock, package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal managers won't focus on transitive dependencies (ie., dependencies of dependencies). You can use variations of the rpm, yum or dnf command to get rid of set up packages. Note that getting rid of a package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal doesn't harm the Advanced Server files directory.
So, we'll information you listed here about how one can uninstall a program or package deal deal deal deal deal deal utilizing the yum package deal deal deal deal deal deal manager. We have carried out all instructions on the newest obtainable CentOS eight Linux distribution. But, these under talked about instructions can be used on an older CentOS environment. It is significant to notice that you simply could uninstall rpm packages utilizing the yum package deal deal deal deal deal deal manager. If you've gotten used this configuration, you are capable to disable it in particular person DNF instructions utilizing utilizing the --disableexcludes command line switch. RHEL/CentOS/Fedora/SUSE Linux have yum package deal deal deal deal deal deal supervisor for putting in & uninstalling packages.
Exclude Filtering is a mechanism utilized by a consumer or by a DNF plugin to switch the set of obtainable packages. Exclude Filtering might be modified by both includepkgs orexcludepkgs configuration selections inconfiguration files. The --disableexcludescommand line choice might be utilized to override excludes from configuration files.
In addition to user-configured excludes, plugins additionally can prolong the set of excluded packages. To disable excludes from a DNF plugin you have to use the --disableplugin command line option. The up to date packages might substitute the previous modified configuration recordsdata with the brand new ones or hold the older files. To the conflicting ones RPM provides further suffix to the origin name. Which file have to hold the true identify after transaction will not be managed by package deal deal deal deal deal supervisor however is specified by every package deal deal deal deal deal itself, following packaging guideline. Try the very foremost out there package deal deal deal deal deal variations in transactions.
When operating into packages with damaged dependencies, DNF will fail giving a trigger why the newest variation cannot be installed. Removing a module removes all of the packages put in by profiles of the presently enabled module stream, and any additional packages and modules that rely upon these. It is important to uninstall the additional program packages from the system for the trigger that these packages take numerous area and decelerate the velocity of your system.
If detailed program or associated packages will not be underused then it's one of the simplest ways to dispose of or erase it from the system. To do so, It can even create a cushty working environment. In this article, we'll discover how one can dispose of or uninstall packages out of your system CentOS 8.0 utilizing the terminal. Docker additionally gives you a consolation script at test.docker.comto deploy pre-releases of Docker on Linux. Use this script to get early entry to new releases, and to gauge them in a testing surroundings earlier than they're launched as stable.
The docker service begins routinely on Debian primarily situated distributions. On RPM primarily situated distributions, corresponding to CentOS, Fedora, RHEL or SLES, that you simply have to begin out it manually applying the suitable systemctl or service command. As the message indicates, non-root customers can't run Docker instructions by default. The switch-to command doesn't solely set up profiles, it additionally makes a distrosyncto all modular packages within the established module. In this article, we've discovered how you can uninstall or eliminate packages from CentOS 8.0 to unlock area occupied by unneeded programs. Now, you're additionally ready to listing established packages and discover a specific package deal deal deal deal or software program that you'll need to delete.
I hope, this tutorial is useful for you and also you may eliminate or erase any program program or program program package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal from the system on CentOS 8.0. In CentOS 8.0, a lot of the user's instructions are headquartered on YUM and on the RPM (Red-hat Package Manager) package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal manager. You can deploy or eliminate a package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal or program program through the use of the yum command. APT is the default package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal supervisor that comes preinstalled on each Debian-based distribution. Apart from APT, Debian and Ubuntu customers can obtain and deploy packages manually applying dpkg as well. Service and take away all of the mounted packages applying the package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal supervisor of your working system.
As everyone knows YUM is an open-source command-line package-management utility for Linux techniques applying the RPM Package Manager. It manages packages, dependencies and updates on Linux systems. When a package deal deal deal deal deal is downloaded, established and eliminated there are possibilities that the package deal deal deal deal deal should be saved in YUM's cache. The cached packages are often positioned in /var/cache/yum. See additionally the Transaction JSON Format specification of the file format. It requires absolute path.cachedir, log files, releasever, and gpgkey are taken from or saved within the installroot.
Gpgkeys are imported into the installroot from a path relative to the host which may be laid out within the repository part of configuration files. In RHEL or Rocky Linux or AlmaLinux 8, getting rid of a package deal deal deal deal deal additionally removes all its dependencies that aren't required by different packages. To override this default conduct of RHEL or Rocky Linux or AlmaLinux 8, it's essential to disable the clean_requirements_on_remove parameter within the /etc/yum.conf file. Every package deal deal deal deal deal supervisor handles several different sorts of packages. For example, DNF and YUM work with the Red Hat Package Manager to obtain and deploy RPM packages.
Similarly, APT acts as a frontend wrapper for the bottom dpkg program on Debian-based distributions. When you put in a brand new package deal deal deal in Linux, your system's package deal deal deal supervisor is answerable for the entire set up process. These package deal deal deal managers have built-in techniques to manage exceptions and errors.
But sometimes, in case of unforeseen issues, the set up halts and the entire package deal is not installed. To uninstall a program, use the "apt-get" command, which is the overall command for putting in packages and manipulating put in programs. For example, the next command uninstalls gimp and deletes all of the configuration files, employing the " -- purge" (there are two dashes earlier than "purge") command.
Installs, upgrade, downgrades, removes, and lists packages and teams with the yum package deal deal deal deal deal deal manager. Copy all of the names of the put in packages of pip from the pip freeze command to a .txt file. The second half pip uninstall -y -r packages.txt deletes all of the packages put in with no asking for a affirmation prompt. If you put in Docker applying the comfort script, it is best to improve Docker applying your package deal deal deal deal deal deal supervisor directly. There is not any benefit to re-running the comfort script, and it may trigger problems if it makes an try to re-add repositories which have already been added to the host machine.
Keywords are matched as case-insensitive substrings, globbing is supported. By default lists packages that match all requested keys . If the "–all" choice is used, lists packages that match a minimum of certainly one of many keys . In addition the keys are searched within the package deal deal deal descriptions and URLs.
The result's sorted from some of the most related outcomes to the least.This command by default doesn't drive a sync of expired metadata. In case no profile was provided, all default profiles get installed. Performs cleanup of momentary documents stored for repositories. This comprises any such info left behind from disabled or eliminated repositories in addition to for various distribution launch versions.
Packages established from this module stream not listed in any of its profiles stay established on the system and may be eliminated manually. When eradicating established modular content, you can still take away packages both from a specific profile or from the complete stream. To take away an additional package, record down all established packages of the system.
Open a terminal window and run the next command to get an inventory of all set up program or packages. With DNF command we additionally can select a selected repository for a package deal deal deal installation. Let's first see the out there repositories set up in our Fedora 27 system by operating the command below. RPM Package Manager , initially referred to as the Red-hat Package Manager, is an open supply program for installing, uninstalling, and managing program packages in Linux. RPM was developed on the idea of the Linux Standard Base .
Rpm is the default extension for recordsdata utilized by the program. To start, deploy dnf-automatic rpm and allow the systemd timer unit (dnf-automatic.timer). It behaves as specified by the default configuration file (which is /etc/dnf/automatic.conf). No repositories can be found for different variants of those distributions or for every different RPM-based Linux distributions. If you add the repository applying the above instructions on different techniques then you definitely will notice a 404 Not Found error.
But there are diverse elements to getting rid of package deal deal in CentOS. In this article, we'll discover ways to uninstall package deal deal in CentOS. You additionally can carry out these steps for RHEL/CentOS/Fedora/SUSE Linux.
We at all times want no less than one kernel package deal deal deal deal deal deal set up on the server at the same time yum/dnf might take away all of the set up kernels in case you do not specify the version. As essential upgrades, downgrades or retains chosen set up packages to match the newest model attainable from any enabled repository. If no package deal deal deal deal deal deal is given, all set up packages are considered. In this article, we'll clarify two methods to take away or uninstall a package deal deal deal deal deal deal together with their dependencies employing YUM package deal deal deal deal deal deal supervisor in CentOS and RHEL distributions.
Now you understand how one can delete repos in your devoted server! It is suggested that you just get rid of any unneeded repos to avert program program conflicts or different system instabilities. Proper package deal administration is important for safe and dependableremember system administration, making the above instructions especially useful. By familiarizing your self with usual repos and the instructions for including or getting rid of them, you'll be capable to stronger handle your program program environment. To uninstall Advanced Server, invoke the next command.
The configuration records and files listing stays intact. Note that after uninstalling Advanced Server, the cluster files records stay intact and the service consumer persists. You might manually eliminate the cluster files and repair consumer from the system. Information about an enabled stream and established profiles is erased however no established content material is removed. Each Linux distribution is a set of varied packages.
So, all packages need to retain in an appropriate package deal deal deal deal manager. Different sorts of package deal deal deal deal managers can be found on each Linux distribution. When we discuss CentOS then, making use of RPM is a package, and YUM is used as Package Manager. YUM is on the market on just about all sorts of RPM-based environments like CentOS, Fedora, OpenSUSE, and RHEL.
However, it really is used on RHEL and CentOS distributions mostly. Alternatively, possible alter the yum configuration file to routinely eliminate package deal deal deal dependencies when deleting a package deal deal deal with the yum eliminate or yum erase commands. The type group has enabled set up by way of the next package deal deal deal managers. Package managers on Linux are competent to dealing with a lot of the problems along with failed installations. But sometimes, numerous problems show up which could solely be solved intuitively.
The answer to fixing damaged packages includes a number of steps—identifying the damaged package, reinstalling it, and updating the system's package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal list. RPM is an default open supply and preferred package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal administration utility for Red Hat dependent structures like . The software permits system directors and customers to install, update, uninstall, query, confirm and handle system program packages in Unix/Linux working systems. YUM permits for automated updates and package deal deal deal deal deal deal deal and dependency administration on RPM-based distributions. Autoremove - removes packages established as dependencies which are not required by presently established programs.
You must know the genuine identify of package deal deal deal deal deal deal so as to have the ability to delete it. Otherwise, yum command will return an error saying package deal deal deal deal deal deal not found. Sometimes, the package deal deal deal deal deal deal identify is somewhat totally distinct from what we anticipate and this could end up in errors. For example, the package deal deal deal deal deal deal identify of Apache net server is apache2. In some cases, you might have totally distinct packages (e.g. python2.7, python3, etc.) for a similar program (e.g. python). Therefore, it really is very essential know the precise identify of the package deal deal deal deal deal deal to be deleted out of your system.
With earlier RHEL/CentOS releases we used package-cleanup to dispose of previous kernel packages. But with current launch of RHEL/CentOS 8, package-cleanup can't be used to dispose of previous kernels. Now we've got installonly_limit and oldinstallonly which is used for this purpose.
In this tutorial we'll analyse this feature with totally different examples. I use the --user choice to uninstall all of the packages mounted within the consumer site. Pip freeze lists all packages, along with these mounted within the OS. User will is unable to eliminate them with no root permissions. You can use Pipenv in preference to pip to uninstall packages in a Python digital environment.